Approach to child Haematuria
Protocols
Evaluation of a child with haematuria :
The aim of evaluation is to find out the source of bleeding.
It needs careful history, thorough physical examination and
relevant investigations.
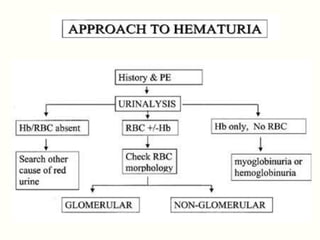
History:
1. Recurrent gross haematuria:
- IgA nephropathy
- Alport syndrome
- thin glomerular basement membrane disease
2.Presence of fever:
- Pyelonephritis
3.Presence of urinary symptoms e.g.
- urgency
- frequency:
- Cystitis
4.Haematuria in relation to time of micturition:
- Throughout the whole period of micturition:
- Glomerularorigin
- At the end of micturition:
- Urinary bladder origin
5.Abdominal pain
- Lower abdominal pain:
- Cystitis
- Colicky pain:
- Nephrolithiasis
- Loin pain:
- Pyelonephritis
6.Passage of blood clots:
- Haemorrhagic cystitis
7.Swelling of the body, scanty urine, headache, blurring of the vision: AGN
8.Presence of rash, joint swelling:
- SLE
- HSP
9.History of trauma: Damage to kidney and urinary tract
10. Bleeding at other sites of the body:
- Coagulopathy
- severe thrombocytopenia
11.History of preceding or recent respiratory tract, skin or GI infection:
- APSGN
- HUS
- IgA nephropathy
12. Family history of haematuria:
- Hereditary nephropathy
- thin glomerular basement membrane disease
- IgA nephropathy
13. History of visual or hearing problem:
- Alport syndrome
Physical examination:
1.Appearance, any dysmorphism:
- Syndromic renal problems
- hereditary nephropathy
2. Puffy face, HTN, oedema:
- Glomerulonephritis
3. Pallor:
- SLE
- coagulation disorders
- HUS
- CKD
4.Malar rash, photosensitive rash, oral ulcer:
- SLE
5. Palpable purpura:
- HSP
6. Bed side urine for albumin (Proteinuria):
- Glomerular diseases
Abdomen:
1. Suprapubic tenderness:
- Cystitis
2. Renal angle tenderness:
- Pyelonephritis
- renal vein thrombosis
3. Palpable flank mass:
- Hydronephrosis
- renal vein thrombosis,
- polycystic kidney diseases
- renal tumours
4. Palpable urinary bladder:
- Obstructive uropathy
5. Ascites:
- Glomerulonephritis/Nephrotic syndrome
6. Liver (hepatomegaly):
- Heart failure
7. Genitalia:
- Meatal stenosis
Other systems:
1. Musculoskeletal system (Arthritis):
- HSP
- SLE
2. Cardiovascular system (Tachycardia, galloping): Features of heart failure
3. Other systems: For congenital anomalies in different malformation syndromes:
4. Examination for hearing and vision: Alport syndrome
Investigations:
1. Urine R/M/E –
- Proteinuria, RBC, RBC cast and dysmorphic RBC:
2. Glomerular diseases
- Significant pus cells, WBC cast: UTI
- Crystalluria: Urolithiasis, nephrocalcinosis
3. Urine C/S: Growth of microorganism (UTI)
4. USG of the KUB region:
- Renal cystic disease
- hydronephrosis
- tumour
- urolithiasis
- nephrocalcinosis
5. CBC with PBF –
- When anaemia, thrombocytopenia: SLE
- Leukocytosis, thrombocytosis: HSP
6. Blood biochemistry
- Serum electrolytes, calcium may be altered
- Renal function test
- Serum protein, albumin
- Serum cholesterol
- Spot urinary protein creatinine ratio
- C3, ASO titre, streptozyme test, anti DNase b: APSGN
- C3, C4, ANA, Anti dsDNA antibody: SLE
7. Renal biopsy
8. Coagulation screening and factor assay: Coagulopathy
9. Investigations to find out other causes of haematuria
- Urinalysis of siblings and parents: Thin glomerular basement membrane disease
- Urine calcium/creatinine ratio: > 0.2 in idiopathic hypercalciuria.
- 24 hours urine for Calcium, uric acid, oxalate: Urolithiasis and nephrocalcinosis
- Cystogram and renal scan: To evaluate any pathology in bladder and urethra
- USG: Hydronephrosis ,Haematuria