Other Conditions
Protocols
DRS ABCDE Mx:(ATLS-Advanced Truma Life Support)
ABCD Mx:
1.A-Airway(Check Nose,oral cavity, Throat & Pharynx for any secretion or vomitus দিয়ে বন্ধ আছে কি না।)
mx:
- 1)clearing airway secretions, vomitus by suction or finger sweep maneuver
- 2)open up the air way by head tilt-chin lift maneuver
- 3)puting airway tube
- 4)ET tube may need to maintain airway
2.B-Breathing (Check Respiratory rate,Flaring of alae,cyanosis,Chest movement, O2 saturation)
mx:if pt caynosis or dyspnoea
1)O2 inhalation by
- Nasal cannula (1-2L/min) or
- Face mask(5L/min) or
- Bag & Mask ventilation or
- ET intubation. Or
- Mechanical Ventilation
3.C-circulation ( check Pulse,BP,pulse pressure, CRT,ECG)
Mx: Do I/V cannula then start baby saline/Normal saline
if pt is in shock : Low BP + CRT more then 3 seconds
- Give I/V Normal saline bolus (20ml/kg)
- Reassess and if no improve then repeat bolus
If shock persist then give
- inj.Dopamine (10-20microgm/kg/min)
OR
- inj.Dobutamine(10-20microgm/kg/min)
4.D-Disability : ( Neurological status of Pt like Alert,cerebral pain,consciousness, response)
Mx:
- GCS
- Check pupil
- Identify any paralysis
5.E-Exposure:
- Completely undress the patients and assess for other injuries.
- 1)pre- hospital stage
- 2)At scene of truma
- 3)on arrival at the receiving hospital

Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR):( পাশে ছবি গুলো খেয়াল করুন)
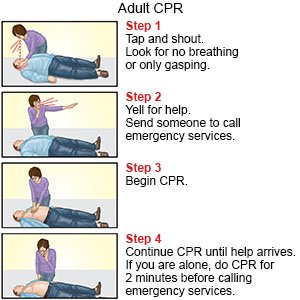
CPR step-by-step
There are two main stages to CPR: the preparation stage and the CPR stage.
Preparation steps:
Before performing CPR on an adult, use the following preparation steps:
Step 1. Call emergency :
First, check the scene for factors that could put you in danger, such as traffic, fire, or falling masonry. Next, check the person. Do they need help? Tap their shoulder and shout, “Are you OK?”
If they are not responding, call emergency number or ask a bystander to call emergency number before performing CPR. If possible, ask a bystander to go and search for an AED machine. People can find these in offices and many other public buildings.(প্রথমে, ট্র্যাফিক, আগুন, বা রাজমিস্ত্রির পতনের মতো আপনাকে বিপদে ফেলতে পারে এমন কারণগুলির জন্য দৃশ্যটি পরীক্ষা করুন। পরবর্তী, ব্যক্তি পরীক্ষা করুন. তারা সাহায্য প্রয়োজন? তাদের কাঁধে আলতো চাপুন এবং চিৎকার করুন, "আপনি ঠিক আছেন?"
যদি তারা সাড়া না দেয়, জরুরী নম্বরে কল করুন বা সিপিআর সম্পাদন করার আগে একজন দর্শককে জরুরি নম্বরে কল করতে বলুন। যদি সম্ভব হয়, একজন দর্শককে যেতে এবং একটি AED মেশিন অনুসন্ধান করতে বলুন। লোকেরা অফিস এবং অন্যান্য অনেক পাবলিক বিল্ডিংয়ে এগুলি খুঁজে পেতে পারে)
Step 2. Place the person on their back and open their airway
Place the person carefully on their back and kneel beside their chest. Tilt their head back slightly by lifting their chin.
Open their mouth and check for any obstruction, such as food or vomit. Remove any obstruction if it is loose. If it is not loose, trying to grasp it may push it farther into the airway.(ব্যক্তিটিকে তাদের পিছনে রাখুন এবং তাদের শ্বাসনালী খুলুন
ব্যক্তিটিকে সাবধানে তাদের পিঠে রাখুন এবং তাদের বুকের পাশে হাঁটু গেড়ে রাখুন। তাদের চিবুক তুলে তাদের মাথা কিছুটা পিছনে কাত করুন।
তাদের মুখ খুলুন এবং খাবার বা বমির মতো কোনো বাধা আছে কিনা তা পরীক্ষা করুন। কোনো বাধা ঢিলে হলে তা সরিয়ে ফেলুন। যদি এটি আলগা না হয় তবে এটিকে বোঝার চেষ্টা করলে এটি শ্বাসনালীতে আরও দূরে ঠেলে দিতে পারে।)
Step 3. Check for breathing
Place your ear next the person’s mouth and listen for no more than 10 seconds. If you do not hear breathing, or you only hear occasional gasps, begin CPR.
If someone is unconscious but still breathing, do not perform CPR. Instead, if they do not seem to have a spinal injury, place them in the recovery position. Keep monitoring their breathing and perform CPR if they stop breathing.(ব্যক্তির মুখের পাশে আপনার কান রাখুন এবং 10 সেকেন্ডের বেশি শুনুন না। আপনি যদি শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাস শুনতে না পান, বা আপনি কেবল মাঝে মাঝে হাঁফ শুনতে পান, তাহলে CPR শুরু করুন।কেউ অজ্ঞান হয়ে গেলেও শ্বাস নিচ্ছেন, সিপিআর করবেন না। পরিবর্তে, যদি তাদের মেরুদণ্ডের আঘাত বলে মনে না হয় তবে তাদের পুনরুদ্ধারের অবস্থানে রাখুন। তাদের শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাসের উপর নজর রাখুন এবং তাদের শ্বাস বন্ধ হলে সিপিআর করুন)
Step 4. Perform 30 chest compressions:
Place one of your hands on top of the other and clasp them together. With the heel of the hands and straight elbows, push hard and fast in the center of the chest, slightly below the nipples.
Push at least 2 inches deep. Compress their chest at a rate of least 100 times per minute. Let the chest rise fully between compressions.
(আপনার একটি হাত অন্যটির উপরে রাখুন এবং তাদের একসাথে আঁকড়ে ধরুন। হাতের গোড়ালি এবং সোজা কনুই দিয়ে, বুকের মাঝখানে, স্তনবৃন্তের সামান্য নীচে শক্ত এবং দ্রুত ধাক্কা দিন। কমপক্ষে 2 ইঞ্চি গভীরে ধাক্কা দিন। প্রতি মিনিটে কমপক্ষে 100 বার হারে তাদের বুককে সংকুচিত করুন। কম্প্রেশনের মধ্যে বুক সম্পূর্ণভাবে উঠতে দিন।)
Step 5. Perform two rescue breaths
Making sure their mouth is clear, tilt their head back slightly and lift their chin. Pinch their nose shut, place your mouth fully over theirs, and blow to make their chest rise.
If their chest does not rise with the first breath, retilt their head. If their chest still does not rise with a second breath, the person might be choking.(তাদের মুখ পরিষ্কার আছে তা নিশ্চিত করে, তাদের মাথাটি কিছুটা পিছনে কাত করুন এবং তাদের চিবুকটি তুলুন। তাদের নাক চিমটি বন্ধ করুন, আপনার মুখটি সম্পূর্ণরূপে তাদের উপরে রাখুন এবং তাদের বুকের উপরে ঘা দিন।যদি তাদের বুক প্রথম নিঃশ্বাসে উঠতে না পারে তবে তাদের মাথাটি উলটান। যদি তাদের বুক এখনও দ্বিতীয় নিঃশ্বাসে না ওঠে, তবে ব্যক্তিটি দম বন্ধ হয়ে যেতে পারে।)
Step 6. Repeat
Repeat the cycle of 30 chest compressions and two rescue breaths until the person starts breathing or help arrives. If an AED arrives, carry on performing CPR until the machine is set up and ready to use.(30টি বুকের কম্প্রেশন এবং দুটি রেসকিউ শ্বাসের চক্রটি পুনরাবৃত্তি করুন যতক্ষণ না ব্যক্তি শ্বাস নিতে শুরু করে বা সাহায্য না আসে। যদি একটি AED আসে, মেশিন সেট আপ এবং ব্যবহারের জন্য প্রস্তুত না হওয়া পর্যন্ত CPR সম্পাদন চালিয়ে যান।)
Clinical Features:
- continuous seizure or convulsion more then 30 min
Investigations:
- 1)CBC
- 2)CSF study
- 3)Serum calcium
- 4)RBS
- 5)Serum Mg
- 6)ABG
- 7)CT Screen of brain
- 8)EEG
Rx:
Algorithrm:
At 1st check CBG if pt hypoglycemic then manage accordingly.
1)ABC management
A-Airway(Check Nose,oral cavity, Throat & Pharynx for any secretion or vomitus দিয়ে বন্ধ আছে কি না।)
➡️mx:
- 1)clearing airway secretions, vomitus by suction or finger sweep maneuver
- 2)open up the air way by head tilt-chin lift maneuver
- 3)puting airway tube
- 4)ET tube may need to maintain airway
B-Breathing (Check Respiratory rate,Flaring of alae,cyanosis,Chest movement, O2 saturation)
➡️mx:if pt caynosis or dyspnoea
1)O2 inhalation by
- - Nasal cannula (1-2L/min) or
- -Face mask(5L/min) or
- -Bag & Mask ventilation or
- -ET intubation. Or
- - Mechanical Ventilation
C-circulation ( check Pulse,BP,pulse pressure, CRT,ECG)
➡️Mx: Do I/V cannula then start baby saline/Normal saline
💉if pt is in shock : Low BP + CRT more then 3 seconds
- Give I/V Normal saline bolus (20ml/kg)
- Reassess and if no improve then repeat bolus
💉If shock persist then give
- inj.Dopamine (10-20microgm/kg/min)
or
- inj.Dobutamine(10-20microgm/kg/min)
Control convulsion : (এখানের সকল drugs এর dose pediatric drugs & dose অংশে দেওয়া আছে)
1) Per Rectal [post id="476" title="Diazepam"] (sedil), (0.1ml×Kg) (maximum 20mg)
⬇️if convulsion persist
If convulsion, then Repeat Per rectal Diazepam after 10 min
⬇️if no response
I/V inj.Fosfen(Fosphenytoin) drip 20mg/kg over 10-30 min
⬇️if convulsion persist
Inj.Barbit([post id="496" title="Phenobarbitone"]) 20mg/kg
⬇️if convulsions persist
Inj.Midazolam (0.2mg/kg) bolus
⬇️if convulsions persist
Then give antiepileptic drugs like inj.Levetiracetum(iracet),inj.Na valproate(valex)
Referred pt higher centre...
🌎🌎সময়ই জীবনের সবচেয়ে বড় শিক্ষক, কারণ সময় যা শেখায় তা আর কেউ শেখাতে পারে না।🌎🌎
Bee bite/ Anaphylaxis:
Investigation:
- 1)Serum IgE
- 2) skin prick test
Rx:
- Removal of underlying cause .eg-removal of bee sting
- Ensure airway patency
- Positon of pt lying flat with feet raised
- 02 inhallation 4L/min
- Nebulization é sultolin stat & sos
1. Inj. cotson (100mg)(Hydrocortisone)
- 1vial I/V stat & sos
2.Inj. Avil(45.4/2ml)(Pheniramine)
- 1 amp l/M stat & sos
3. Tab. Fenadin(Fexofenadine) (120mg)/ Rupa (10mg)(rupatadine)
- 0+0+1….7 days
If pain:
1. Tab. Torax (10mg)(Ketorolac)
- 1+0+1.....3 days(ভরাপেটে)
2. Tab. Maxpro (20mg)(Esomeprazole)
- 1+0+1.( খাবার ৩০ মি আগে).....7 days
if itching:
Togent ointment
- চুলকানির জায়গায় দিনে ৩ বার....৭ দিন
If Restlessness:
Inj. sedil(Diazepam)(10mg/2ml)
- 1 amp I/M stat & sos
if patient condition is not improved then referred.
Prevention:
- Cover exposed skin.
- Wear shoes when outdoors.
- Apply insect repellent.
- Avoid using products with strong perfumes.
- Avoid flowering plants, outdoor areas where food is served, rubbish and compost areas.
- Remove and destroy insect nests.
- Avoid flea infestations.
Clinical Features:
- 1)Rapid breathing.
- 2)Severe shortness of breath.
- 3)Sudden, rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- 4)Loss of consciousness.
- 5)Weak pulse.
- 6)Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- 7)Sweating.
- 8)Pale skin
Investigations:
- 1)ECG
- 2)Echocardiography
- 3)Chest X-ray P/A View
- 4)CBC
Rx:
- Absolute Bed Rest( rise foot end)
- High flow o2 inhalation(2-4 L)
- Diet-liquid
- cardiac monitoring
- maintain I/V channel (5% DA)
1.Inj. Dopamine 2 amp + 500 ml N/S @ 32 microdrop/min
2. Tab.[post id="860" title="Aspirin"](Carva)(75mg) 4 tab orally stat by crushing Then 0+1+0(after meal)...চলবে
3.cap.[post id="393" title="Pantoprazole"](pantonix) (20mg) 1+0+1(before meal) ...১ মাস
4.Tab.[post id="476" title="Diazepam"](sedil) (5 mg) 0+0+1….1 মাস
Monitor vitals sign following of cardiogenic shock
- ECG
- BP
- URINE OUTPUT
- Skin temperature
- central venous pressure
- 02 saturation
Hypovolumic shock :
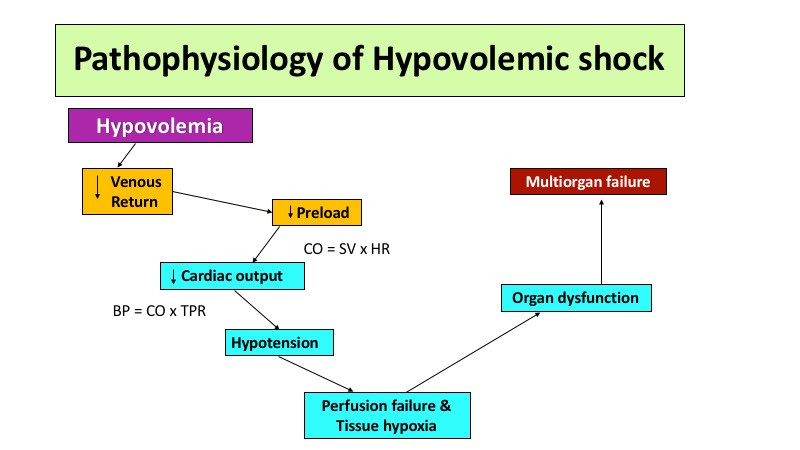
Symptoms:
- 1)Anxiety or agitation.
- 2)Cool, clammy skin.
- 3)Confusion.
- 4)Decreased or no urine output.
- 5)Generalized weakness.
- 6)Pale skin color (pallor)
- 7)Rapid breathing.
- 8)Sweating, moist skin.
Signs:
- 1)tachycardia,
- 2)decreased systolic BP,
- 3)narrowed pulse pressure (or immeasurable diastolic pressure),
- 4) markedly decreased (or no) urinary output,
- 5) depressed mental status (or loss of consciousness), and cold and pale skin.
Investigations:
- 1) cbc
- 2)RBS
- 3)serum Creatinine
- 4)ECG
- 5)CRT
Mx:
1) Commence high-dose oxygen via a face mask. Maintain the oxygen satura-tion above 94%.
2) Compress or pack any extcrnal haemorrhage such as cpistaxis or wound blccding.
3) Begin immediate fluid replacement:
- (1️⃣) Give 20 mL/kg normal saline iv. rapidly and repeat , aiming for a urinc output of 0.5-1 mL/kg per /hours
- (a) then gradually correct any dehydration (rehydration), and include _daily ; maintenance amounts.
- (2️⃣) Give cross-matched blood when it is available, if the patient is shocked due to blood loss
- (a) remember that in healthy adults the only signs associated with loss of up to 30% of the circulatory blood volume (i.e. 1500 mL) may be a tachycardia and a narrowed pulse pressure
- (b) thus, a consistent fall in SBP indicates that at Ieast 30% of the blood volume has already been lost
- (c) full cross-match takes 45 min, a Type specific cross-match takes 10 min, and O rhesus-negative blood is _ available immediately
- (d) use a blood warmer and macropore blood filter for multiple transfusions ~
- give fresh frozen plasma 8-10 units and platelets after trans-fusing 8-10 units of blood or more, i.e. in a 1:1 ratio for a “Massive blood transfusion’
- (e) aim for haemoglobin 70-100 g/L, or haematocrit more then 30%,
4) Consult the surgical, vascular or gynaccological team immediately if there is suspected blood loss causing shock (e.g. ruptured spleen, AAA or ectopic pregnancy).
5)Admit the patient to theatre, intensive care unit (ICU) or a high-dependency unit (HDU) depending on the underlying cause, and response to treatment.
Clinical features:
- 1)Cool, pale arms and legs.
- 2)High or very low temperature, chills.
- 3)Lightheadedness.
- 4)Little or no urine.
- 5)Low blood pressure, especially when standing.
- 6)Palpitations.
- 7)Rapid heart rate.
- 8)Restlessness, agitation, lethargy, or confusion.
Investigations:
- 1)CBC with ESR with CRP
- 2)CXR
- 3)ECG
- 4)urine RME
- 5)serum creatinine
- 6)pregnancy test
- 7)LP
- 8)RBS
- 9)serum electrolyte
Mx:
1)Commence high-dose oxygen via a face mask. Maintain the oxygen satura-tion above 94%.
2)Begin aggressive fluid replacement:
- Give 20 mL/kg normal saline i.v. rapidly over the first 30 min and then reassess. Multiple boluses may be required
- (a) intravascular fluid resuscitation often requires large volumes up to 50-100 mL/kg before volume replacement is adequate
- (b) censure hacmoglobin is maintained above 100 g/L.
3)Administer appropriate antibiotics early. Mortality is reduced if antibiotics are given within 1 h of onset of hypotension.
- Each additional hour of delay adds 7% to the mortality in septic shock.
- Get senior advice early and consult local antibiotic guidelines:
(i) Give flucloxacilln 2 g iv. qd. plus gentamicin 5mg/kg once daily if no source is apparent in the immunocompctent paticnt.
(ii) Add vancomycin 1.5 g iv. 12-hourly for possible MRSA including community. associated (CA-MRSA), suspected line scpsis and instcad of flucloxacillin for immediate hypersensitivity.
(iit) Give neutropenic patients piperacillin 4 g with tazobactam 0.5 g i.v. 8-hourly, plus gentamicin 5 mg/kg stat when no source is apparent, and add vancomycin 1.5 g iv. 12-hourly for possible linc sepsis.
(iv) Otherwise give antibiotics to cover likely pathogens depending on a known focus, and/or once culture and scnsitivitics are known.
4)Start vasopressor support for continuing hypotension despite fluid resusci-tation.
- (1) Give noradrenalinc or adrenaline iv. by infusion to maintain mean artcrial pressure (MAP) more 65 mmHg.
- (ii) Inotropic support with dobutamine iv. by infusion may also be required, as myocardial depression is common in severe sepsis.
- (iii) Give hydrocortisone 50 mg i.v. q.d.s. if poorly responsive to fluid and vasopressor therapy.
5) Refer the patient urgently to the surgical team if a local cause requires source control or drainage such as wound debridement, laparotomy for perforation, percutaneous drainage for urinary obstruction, etc. Contact theatre and the anaesthetist.
6)Meanwhile arrange admission to ICU for all Paticnts.

Anaphylactic shock:
Investigation:
- 1)Serum IgE
- 2) skin prick test
Rx:
- Removal of underlying cause .eg-removal of bee sting
- Ensure airway patency
- Positon of pt lying flat with feet raised
- 02 inhallation 4L/min
- Nebulization é sultolin stat & sos
1. Inj. cotson(Hydrocortisone) (100mg/2ml)
- 1vial I/V stat & sos
2.Inj. Avil(Pheniramine) (45.5mg/2ml)
- 1 amp l/M stat & sos
3. Tab. Fenadin (Fexofenadin) (120mg)/ Rupa (Rupatadine) (10mg)
- 0+0+1….7 days
If pain:
Tab. Torax (Ketorolac)(10mg)
- 1+0+1.....3 days(ভরাপেটে)
Tab. Maxpro (Esomeprazole)(20mg)
- 1+0+1.( খাবার ৩০ মি আগে).....7 days
If Restlessness:
Inj. sedil (Diazepam)(10mg/2ml)
- 1 amp I/M stat & sos
if patient condition is not improved then referred.
Prevention:
- Avoid your allergens.
- Take your medicines as prescribed.
- If you are at risk for anaphylaxis, keep your epinephrine auto-injectors with you at all times.
- Keep a diary.
- Wear a medical alert bracelet (or necklace).
- Know what to do during an allergic reaction.
Clinical Features:
- 1)sweating.
- 2)feeling tired.
- 3)dizziness.
- 4)feeling hungry.
- 5)tingling lips.
- 6)feeling shaky or trembling.
- 7) fast or pounding heartbeat (palpitations)
- 8)becoming easily irritated, tearful, anxious or moody.
investigation:
- 1)RBS
- 2)serum calcium
- 3)serum electrolyte
Rx:
- complete bed rest
- o2 inhalation
if Pt Shock / Coma তে থাকলে :
- Inf. 25% Nutridex (100ml) 1/ Running - stat
Then
- 10% DA ([post id="511" title="Dextrose "])(1L) I/V@ 10d/min - 24h
Special note:
- Coma তে গেলে ১দিন diabetic drug বন্ধ।
- Pt Conscious থাকলে hypoglycaemia র symptoms দেখা দিলে কাছে যা পাবে তাই খাবে (চিনি, গুড়, চকলেট, ভাত, কলা ইত্যাদি)।
Prevention Hypoglycemia:
- Monitor your blood sugar.
- Don't skip or delay meals or snacks.
- Measure medication carefully, and take it on time.
- Adjust your medication or eat additional snacks if you increase your physical activity.
- Eat a meal or snack with alcohol, if you choose to drink.
- Record your low glucose reactions.
causes of Epistaxis:
- 1)idopathic
- 2)sinositis
- 3)rhinitis
- 4)truma
- 5)Foreigh body
- 6)HTN
- 7)Leukemia
Clinical Features:
- BLOOD FROM NOSE
INVESTIGATIONS:
- 1)Couagulation Profile(
- BT
- CT
- PT
- APTT
- 2)CBC
- 3)Upper GI Endoscopy
Rx:
- Diet: Normal
If H/O Trauma:
- Pressure over(10 min) the Ala of nose/ Ice over the Ala of nose.
Active bleeing :
If Not Controlled bleeding
⬇️
Exam under G/A
Bleeding point ➡️if found (electrocauterization)
⬇️If not found bleeding point
ANS Pack
⬇️If not stop bleeding
PNS pack
⬇️If not stop bleeding
Arterial ligations
⬇️if not stop bleeding
ECA
1. Inj. Xamic (TRANEXAMIC ACID)(500mg)
- 2amp IV stat & sos
2. Cap. Amoxic(Amoxicillin)(500mg)
- 1+1+1...........7 days
3. Rynex 0.1% Nasal drop(oxymetazoline)
- 3 drops each nose 3 times daily.........7 days
4.Tab. Rivo(Clonazepam) (0.5mg)
- 0+0+1........15 days
❤❤. ব্যর্থতাকে ভয় করার বদলে চেষ্টা না করে বসে থাকাকে ভয় করো ।❤❤
Discharge from hospital/ Chamber :
1.Cap.Amoxic(AMOXICIILIN)(500mg)
- 1+1+1…… 7days
2. Antazol (Xylometazoline )0.1% nasal drop /Rynex nasal drop(oxymetazolin)
- 2 drop each nostril * TDS….10 days
3. Tab.Rivo(0.5mg)(clonazepam)
- 0+0+1……...15 days
4.Cap.Xamic(500mg)
- 1+1+1…..3 days(if bleeding)
5.Tab.Fixocard(5/50mg)
- 0+0+1….continue(if HTN)