Physiotherapy
Protocols
About phsiotherapy treatment :
Physiotherapists help people affected by illness, injury or disability through exercise, manual joint therapy,
soft tissue techniques, education and advice. Physiotherapists maintain physical health,
allow patients to manage pain and prevent disease for people of all ages. Physiotherapists
help encourage pain relief, injury recovery, enabling people to stay playing a sport,
working or performing daily living activities while assisting them to remain functionally independent.
There is a multitude of different physiotherapy treatment approaches.
(ফিজিওথেরাপিস্ট ব্যায়াম, ম্যানুয়াল জয়েন্ট থেরাপি, নরম টিস্যু কৌশল, শিক্ষা এবং
পরামর্শের মাধ্যমে অসুস্থতা, আঘাত বা অক্ষমতায় আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তিদের সাহায্য করেন।
ফিজিওথেরাপিস্টরা শারীরিক স্বাস্থ্য বজায় রাখে, রোগীদের ব্যথা পরিচালনা করতে এবং
সব বয়সের মানুষের জন্য রোগ প্রতিরোধ করতে দেয়। ফিজিওথেরাপিস্টরা ব্যথা উপশম,
আঘাতের পুনরুদ্ধারে উৎসাহিত করতে সাহায্য করে, লোকেদেরকে খেলাধুলা করতে, কাজ
করতে বা দৈনন্দিন জীবনযাত্রার ক্রিয়াকলাপ সম্পাদন করতে সাহায্য করে এবং
তাদের কার্যকরীভাবে স্বাধীন থাকতে সহায়তা করে।
বিভিন্ন ফিজিওথেরাপি চিকিত্সা পদ্ধতির একটি ভিড় আছে)
💢Types of physiotherapy :
1️⃣Hands-On Physiotherapy Techniques:
👉Joint Mobilisation (gentle joint gliding techniques)
👉Joint Manipulation
👉Physiotherapy Instrument Mobilisation (PIM)
👉Minimal Energy Techniques (METs)
Massage
👉Soft Tissue Techniques
2️⃣Physiotherapy Taping:
👉Supportive Strapping
👉Kinesiology Taping
👉Alternatively, your physiotherapist may recommend a supportive brace.
3️⃣Acupuncture and Dry Needling:
👉Acupuncture
👉Dry Needling
4️⃣Physiotherapy Exercises:
👉Muscle Stretching
👉Core Exercises
👉Strengthening Exercises
👉Neurodynamics
👉Balance Exercises
👉Proprioception Exercises
👉Real-Time Ultrasound Physiotherapy
👉Swiss Ball Exercises
5️⃣Biomechanical Analysis:
👉Biomechanical Analysis
👉Bike Fit Setup
👉Gait Analysis
👉Video Analysis
6️⃣Hydrotherapy:
7️⃣Sports Physiotherapy:
👉Sports Injury Management
👉Prehabilitation
8️⃣Vestibular Physiotherapy:
👉BPPV Manoeuvres
👉Vestibular Physiotherapy
👉Falls Prevention
9️⃣ Women’s Health:
👉Women’s Health Physiotherapy
👉Pelvic Floor Exercises
🔟Workplace Physiotherapy:
👉Home / Office Workstation Setup
👉Corporate Wellness
👉Workplace Wellness
👉Electrotherapy
👉Electrotherapy & Local Modalities
👉Therapeutic Ultrasound
👉TENS Machines
👉EMS Machines
💢Mulligan Techniques :
💢aim of Mulligan tech:
PILL response is observed for:
P– Pain free.
I– Instant result.
LL– Long Lasting.
Mulligan Manual Therapy
reduces soft tissue inflammation,
induces relaxation and improves function in individuals with musculoskeletal pain.
💢. The second principle is CROCKS[5
C- Contra-indications (No PILL response is a contraindication)
R - Repetitions (Only three reps on the day one)
O- Over pressure
C- Communications
K - Knowledge (of treatment planes and pathologies)
S- Sustain the mobilization throughout the movement.
💢Principles of mulligan concept :
1) passive accessory joint mobilization is applied following the principles
of Kaltenborn. This accessory glide must itself be pain-free.
2)During the assessment, the therapist will identify one or more comparable signs as
described by Maitland. These signs may be; a loss of joint movement, pain associated with
movement, or pain associated with specific functional activities.
3)The therapist must continuously monitor the patient’s reaction to ensure no pain is recreated.
The therapist investigates various combinations of parallel or perpendicular glides to find the
correct treatment plane and grade of accessory movement.
4)While sustaining the accessory glide, the patient is requested to perform the comparable sign.
The comparable sign should now be significantly improved.
5)Failure to improve the comparable sign would indicate that the therapist has not found the correct
treatment plane, grade of mobilization, spinal segment or that the technique is not indicated.
6)The previously restricted and/or painful motion or activity is repeated by the
patient while the therapist continues to maintain the appropriate accessory glide.
💢Indications of Mulligan:
1)The pain of a non-inflammatory nature
2)Acute pain from injury
3)Loss of motion due to arthritic conditions
4)Post-surgical conditions causing loss of
pain-free movement, e.g. post scope conditions, spinal surgery
6)Headaches due to neck problems
7)Dizziness associated with neck problems
8)Jaw or TMJ pain and movement restrictions
9)Acute to chronic ankle sprains
10)Tennis elbow” or lateral elbow pain
💢Contra-indications:
👉Relatives contra-indications
1)joint hypermibility
2)Pregnancy
3) Osteopenia
👉Absolute Contra-indications
1) Bones weakness(osteoporosis, tumor,metabolic bone disease)
2) vascular (Anticoagulant therapy,aortic aneurysm
3)psychological disorder
4)Cervical mylopathy
💢McKenzie concept of physiotherapy :
👉The McKenzie concept has the following benefits:
1)Reduces pain
2)Restores function
3)Advice to maintain pain relief
4)Advice on positioning and posture to prevent reoccurrence
💢Indications:
1)Spinal stenosis
2(Hip disorders
3)Sacroiliac disorders
4)Low back pain in pregnancy
5)Chronic pain syndrome
6)Mechanically inconclusive
7)Mechanically unresponsive radiculopathy
8)Structurally compromised
9)Post-surgical problems
10)Trauma/Recovering trauma.
11):Sciatica problem
💢 Contra-indications :
1) Spinal fracture
2)spinal tumor
3)cauda equina syndrome
4) Spinal infection
Neurodynamics Physiotheray:
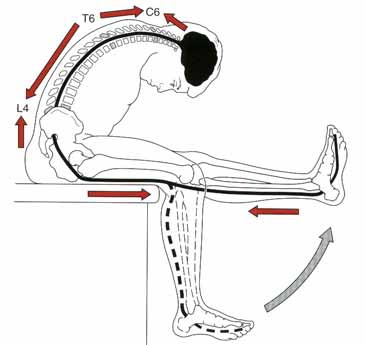
Neurodynamics in the sense implied here is the mobilisation of the nervous system
as an approach to physical treatment of pain. The treatment and or assessment relies
on influencing pain physiology via the mechanical treatment of neural tissues
and non-neural structures surrounding the nervous system.
💢Neurodynamics needs knowledge
1)Neuroanatomy
2)Neurophysiology - study of the function of the nervous system.
3)Neurobiomechanics
4)Neuropathology
🛑Neural examination
1️⃣Traditional examination :
1)Neural Subjective
2)Dermatomes and myotomes
3)Muscle strength
4)Reflexes
5)Romberg’s Test
6)Babinski’s Reflex ( Plantar response)
2️⃣Neural provocation test:
1) ULTT1 (median nerve bias)
2) ULTT2b (radial nerve bias)
3) ULTT3 (ulnar nerve bias)
4) PNF (Lhermitte’s Test)
5) SLR (sciatic, tibial, and peroneal nerve biases)
6) PKB (femoral nerve bias)
7) Slump (dura)
💢Indications:
1)Ankle sprain
2) Cervical and Lumbar Nerve Root Injury
3)Colles Fracture
4)Carpel Tunnel Syndrome
5) Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
6)Hamstring Injury
7) Meralgia Paresthetica
8)Myelopathy
9)Plantarfasciitis
10)Post Lumbar Surgery
11) Whiplash Associated Disorders
12) Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
13) Sciatica
14)Cyclists Palsy
15)Double crush syndrome
16) Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Hydrotherapy :
Hydrotherapy is a popular water-based form of injury and rehabilitation therapy.
💢Indication:
1)Back pain
2)Arthritis (osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, 3)ankylosing spondylitis)
4)Shoulder pain (persistent pain and post-op rehabilitation)
5)Injuries with weight-bearing or loading restrictions
6)Sports injuries where cross-training is required to
maintain fitness (for example, deep water running)
7)Lymphoedema
8)Oedema
9)Fibromyalgia
10)Mobility and balance retraining
11)Chronic pain
12)Chronic fatigue
13)Multiple sclerosis (MS)
14)Parkinson’s disease
15)Pregnancy-related pain (pelvic and back)
16) Autism
💢Contra-indication:
👉Relative Contra-indications :
1)Infections
2)Cardiovascular disease
3)Skin conditions
4)Illness, including common colds and fevers
5)Aquaphobia
6)Labyrinthitis
👉Absolute contraindications :
1)Incontinence
2)Contagious diseases
3)Severe epilepsy
4)Recent surgery
5)Open wounds
6)Urinary tract infection
7)Tracheotomy
8)Recent chemotherapy
Electrotherapy:
A powerful tool used by many physiotherapists, electrotherapy treats chronic pain,
musculoskeletal injuries, muscle wasting, and nerve pain by using targeted and controlled electrical stimulation.
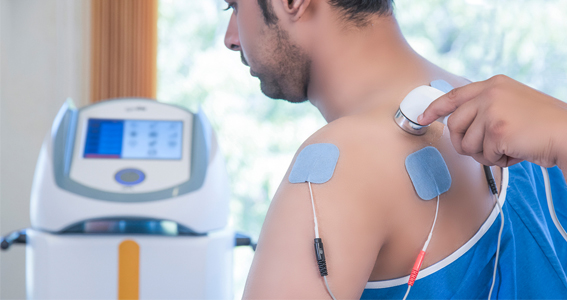
🏵️Types of Electrotherapy: 6 main types
1. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
2. Therapeutic Ultrasound
3. Interferential
4. Electroacupuncture
5. Shockwave Therapy
6. Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
👉Others
✅Micro wave
✅Short Wave
✅Traction bed
✅Infra-red radiation (IRR)
Details above tyoes :
1️⃣Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) :
One of the most common electrotherapy treatments, Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve
Stimulation (TENS) makes use of small devices which deliver pulses of electrical
stimulation. The goal of the TENS machine is to stimulate sensory nerves to
achieve pain relief and is often used for both nerve pain and chronic pain conditions.
2️⃣Therapeutic Ultrasound :
When used in physiotherapy, therapeutic ultrasound in physiotherapy uses a deep
heating effect on different tissues — like muscles, ligaments, and tendons — to
boost circulation and stimulate the healing process. This method makes use of
a transducer instead of electrode pads and is often used to treat strains, tendonitis, and knee meniscus tears.
3️⃣Interferential :
Also known as IFT, interferential electrotherapy uses low-frequency electrical
stimulation to stimulate muscles, increase blood flow, and reduce pain.
IFT is sometimes used for patients who dislike the sensation of TENS electrotherapy.
4️⃣Electroacupuncture :
Ordinarily, acupuncture makes use of thin needles inserted at specific points which
target different organs or bodily systems. Electroacupuncture follows the same principles,
except it uses two needles with an electric current that passes between them.
It's often used to treat chemotherapy side effects and acute pain.
5️⃣Shockwave Therapy :
In shockwave therapy, acoustic waves with high energy are used to treat conditions.
Like therapeutic ultrasound, shockwave therapy makes use of a transducer with gel.
This therapy is used to help stimulate collagen production, release painful trigger
points, and reduce inflammation in the
body. It's also very useful for musculoskeletal conditions like plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, and Achilles tendinopathy.
6️⃣Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) :
While some methods of electrotherapy target nerves, EMS targets muscle tissue.
This specialised form of electrotherapy stimulates your motor neurons which
causes your muscles to contract. This is often used in cases to treat and prevent muscle atrophy.
🏵️Benefits of Electrotherapy in Physiotherapy Treatments :
1. Reduce nerve pain.
2. Promote healing of musculoskeletal injuries.
3. Have a non-invasive, drug-free pain control.
4. Prevent muscle atrophy.
5. Increase circulation for wound repair.
6. Have a minimal to no side effects.
Planter facilities :
💢C/F:
1)Pain on the bottom of the foot near the heel.
2)Pain with the first few steps after getting out of bed in the morning, or after a long
period of rest,such as after a long car ride.
3)Greater pain after (not during) exercise or activity.
💢Risk factor:
1) woman.
2)overweight, obese, or pregnant.
3) between ages 40 and 70.
4)Have flat feet or very high arches.
5)Have tight Achilles tendons.
6)Have an inward pronation (ankle turns inward as you walk)
7)Take part in running, jumping, or dancing such as ballet.
💢investigations: no need its clinical diagnosis.
🏵️Rx:
💊Tab.Naprox([post id="455" title="Naproxen"])(500mg)
১+০+১.......(খাবার পর)....৫-৭ দিন
💊Tab.Relentus (Tizanidine)(2mg)
১+১+১........৩-৫ দিন
💊Cap.Nexum([post id="392" title="Esomeprazole"]) (20mg)
১+০+১......(খাবার ৩০ মি আগে)....১০দিন
👉বেশি ব্যাথা হলে, local Clofenac jel ব্যবহার করতে পারেন।
👉physiotherapy (orthotic, walking boot, splinter,stretch etc)
👉extracorporeal shock wave therapy.
👉 সু- মডিফিকেশন (প্রয়োজনীয় ক্ষেত্রে খুব কাজ দেয়। হিল কুসন সাময়িক আরাম দিলেও
সব সময় কার্যকরী নয়। যেমন ফ্ল্যাট ফুট থাকলে হিল কুশন দিলে হবে না)।
👉👉ইঞ্জেকশন?
যদি উপরের গুলা ফেইল করে, তবে দেয়া যায়। কারো ব্যথা খুব বেশি হলে
তাৎক্ষনিক ব্যথা কমাতেও দেয়া যায়। ভাল কাজ করে স্টেরয়েড ইঞ্জেকশন।
তবে আল্ট্রা গাইডেড না দিলে অনেক রোগির প্লান্টার ফাসা টীয়ার (ফাসাতে ইঞ্জেক্ট করলে) ও ফ্যাট
নেক্রোসিস (ফ্যাটে ইঞ্জেকশন) হতে দেখেছি। প্লান্টার ফাসার ডীপে আলট্রা গাইডেড দেয়া যায়।
👉👉 আর পি.আর.পি?
কিছু RTC হয়েছে যেখানে বলছে শর্ট টার্ম পেইন রিলিফে স্টেরয়েড বেটার।
কিন্তু লংটার্ম রিলিফে (১৮ মাস) পি.আর.পি বেশি কার্যকর।
তাছাড়া পি.আর.পি নিরাপদ। রিজেনারেশন ও হিলিং করে। নন-ইনফ্লেমেটরী টাইপ
(যেটাকে ফাসিওসিস বলেছি, তাতে স্টেরয়েড ইঞ্জকশন ফেইল করতে পারে;
এক্ষেত্রে পি.আর.পি বেশি কার্যকর হবে। ইনফ্লেমেটরি টাইপ ও একিউট কেইসে
স্টেরয়েড বেশি কাজ করবে। ইনক্ল্যামেটরি, ক্রনিক হলেও পি.আর.পি'ই শ্রেয়।
👉surgical :
💉steroid injection in tendon area
💢Advice:
2)put an ice pack (or bag of frozen peas) in a towel on the painful area for
up to 20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours
3)wear shoes with cushioned heels and good arch support
4)se insoles or heel pads in your shoes
5)try regular gentle stretching exercises
6)try exercises that do not put pressure on your feet, such as swimming
7)take painkillers like paracetamol and ibuprofen
8)try to lose weight if you’re overweight
💢এই কাজ গুলো থেকে বিরত থাকুন।
১)do not walk or stand for long periods
২)do not wear high heels or tight pointy shoes
৩)do not wear flip-flops or backless slippers
৪)try not to walk barefoot on hard surfaces
❣️❣️"Keep your face always toward the sunshine, and shadows will fall behind you."❣️❣️
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS):
💢C/F:
1)numbness/tingling/burning/pain
2) shock-like sensations
3)pain and tingling
4)hand weakness and clumsiness
5) dropping things.
💢investigations:
1) Nerve Conduction study
2) EMG
3)X-ray Wrist joint B/V view
🏵️Rx:
👉Rest the Joint
👉Fixed Joint by crape bandage
➡️if pain
💊Tab.Flexi (Aceclofenac) (100mg)
1+0+1.........(after meal).....5 _7 days
💊Tab.Beklo(baclofenc)(10 mg)
1+0+1...........5-7 days
💊Cap.Sergel([post id="392" title="Esomeprazole"]) (20 mg)
1+0+1......(30min before meal)....10 days
🎴Physiotherapy(see pictures) :
👉Wrist raise motion
👉wrist Stretching
👉mid-trap exercise
👉Wrist extension
👉Wrist flexion
👉Grip Strengthening
👉Tendon gridles.